
Arrhythmia in Horses: How Serious Are They?
Arrhythmia, like all cardiac problems in horses, can be very frightening for riders. So this is the opportunity to tell you a little more about these famous arrhythmias in horses, how to detect them and if they are serious or not!
Table des matières
What is an arrhythmia?
Before we begin to detail what an arrhythmia is, it is important to define the terms we are going to use. It is very important to understand the difference between pulse, heart rate, heart rhythm and heartbeat.
Definition: pulse, heart rate, heart rhythm and heartbeat
As you know, the heart contracts and relaxes in a very regular way thanks to its electrical impulses.
A heartbeat therefore corresponds to a cycle [contraction – relaxation]. In more technical terms, we talk about contraction cycles, and even more about systoles (when the heart is contracted and ejects blood) and diastoles (when the heart relaxes to fill with blood).
As for the pulse, it is simply “the perception of the pulsating blood flow from the heart by palpation of an artery.” [1]
Depending on whether the horse is at rest or under stress, calm or stressed, the heart will beat slower or faster. Rather than talking about the speed of the beats, we talk about heart rate.
The heart rate is therefore the number of beats that occur over a given period of time. This heart rate is expressed in beats per minute, or BPM. To measure the heart rate, we use a heart rate monitor.
📚 Learn more: 5 Reasons to use a heart rate monitor with your horse
Finally, the heartbeat corresponds rather to the musical meaning of the term rhythm. The rhythm is the way in which the heartbeats are spaced. Thus, with the same heart rate, the heart rhythm can vary.
A picture is worth a thousand words:
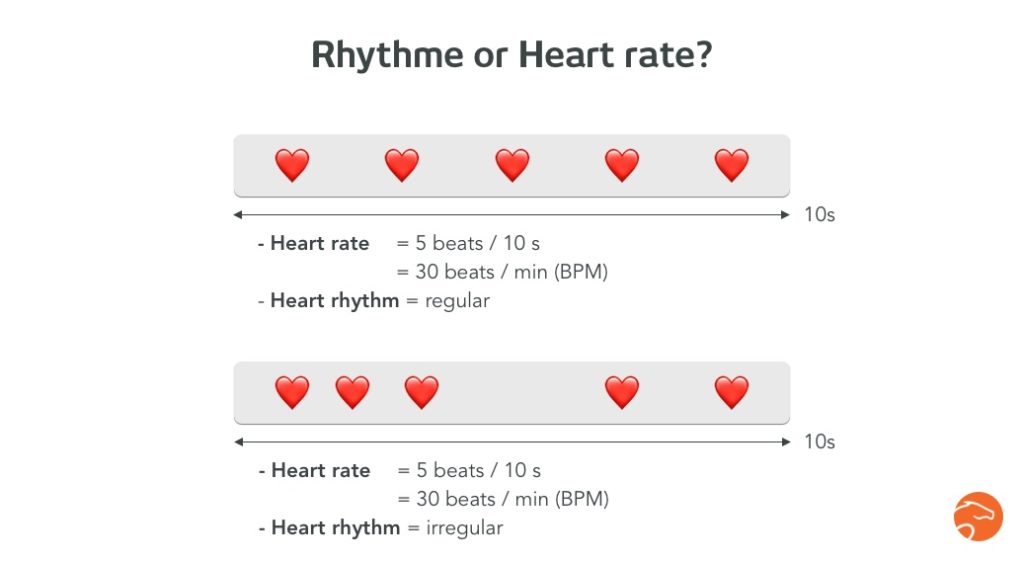
Arrhythmia is a heart rhythm disorder
Thus, an arrhythmia is “a variation in heart rhythm for no apparent reason.”
These variations in heart rhythm can be physiological or pathological. This means that some rhythm disorders are not serious and have no impact on quality of life or sports performance.
Pathological arrhythmias, on the other hand, have potentially significant impacts on quality of life or performance. They become problematic when the muscles and brain are no longer sufficiently supplied with oxygen. Arrhythmias can, for example, lead to significant underperformance or even syncope.
How to detect an arrhythmia in horses?
The ECG, the essential tool for the detection of arrhythmia
First of all, the detection of an arrhythmia can only be done by a veterinarian.
To make the diagnosis, your veterinarian will start by auscultating your horse with a stethoscope. This can only be done at rest.
For a complete diagnosis, a stress test may be necessary. For this, the use of an ECG is required.
ECG stands for Electrocardiogram. It is the measurement of the activity of the heart. The signal recorded by the ECG allows for very precise detection of arrhythmias and their frequency of occurrence.
💡 Did you know?
allows you to measure the electrocardiogram of your horse. Then, you just have to download the file thanks to our webapplication and send it to your veterinarian. They can then analyze it and make recommendations!

Can you detect an arrhythmia on the heart rate?
Indeed, depending on the way the heart rate is calculated and on the tools, it is possible that certain arrhythmias show up on the heart rate.
A high heart rate (>140 bpm) during a low intensity physical effort (relaxation in calm), or a very low heart rate at rest (< 25bpm), should alert you.
If you have the slightest doubt, do not hesitate to talk to your veterinarian.
A few examples of arrhythmias [3]
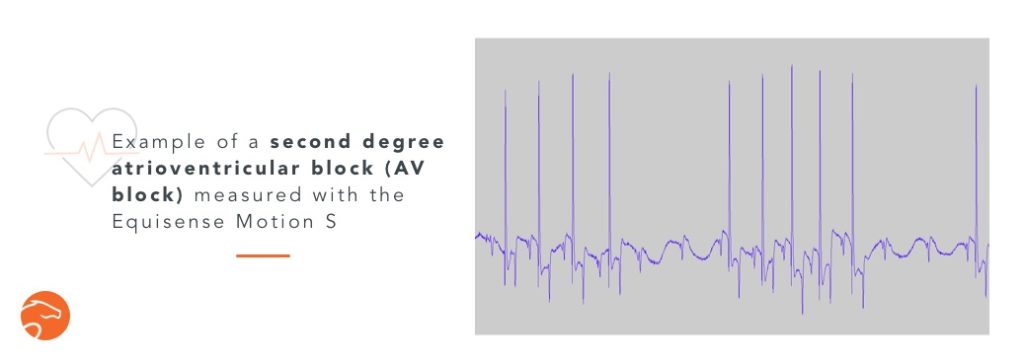
Second degree atrioventricular block (AV block)
This is one of the most common arrhythmias at rest in horses. As the horse has a very low heart rate at rest (~30-40 bpm), sometimes the heart misses a beat, even 2, without any consequence on the horse, provided that these “atrio-ventricular blocks” disappear with effort.
Here’s an example of a second degree AV block measured with the Equisense Motion S :
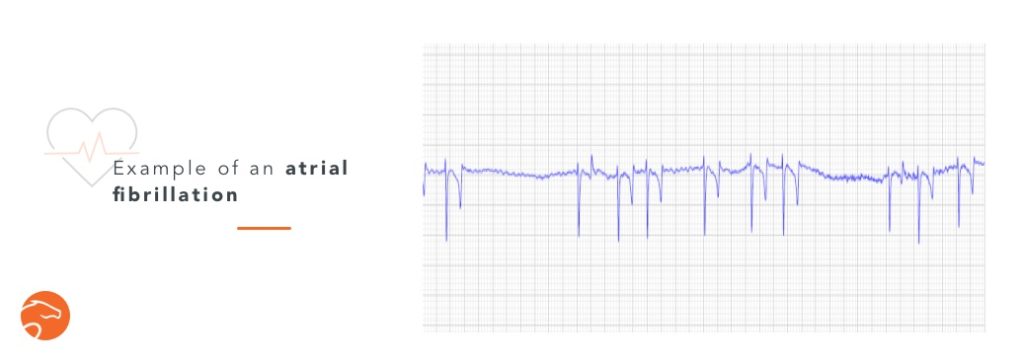
Atrial fibrillation
It is the most common arrhythmia in horses during exercise. One of the elements of the heart contraction is absent from the ECG (the P wave, representing the contraction of the atrium), and the rhythm is irregularly irregular.
Large horses with a large heart are more prone to it. Depending on the underlying cause of the fibrillation, the prognosis is more or less severe.
How serious is it?
The severity of the arrhythmia in horses depends on several factors, including its onset and whether or not it is accentuated by exercise.
If a pathological arrhythmia is detected, the underlying cause must be sought. It is this underlying cause that will determine the severity of the arrhythmia. While some of them can be treated with medication, others are not treatable and have a much worse prognosis.
Only a veterinarian can tell you!
Conclusion
Cardiac arrhythmias are quite common in horses. They are a major reason for intolerance to exercise.
Depending on the type of arrhythmia and its presence or absence during exercise, it can be considered as physiological or pathological.
Regular measurement of the heart rate during exercise can detect variations or abnormal values and can lead the rider to call in the veterinarian for a more precise diagnosis.
See you soon for a new article,
Camille Saute
Co-founder of Equisense and R&D manager
Sources
[1] Wikipédia, “Pouls”, consulté le 2 avril 2021
[2] Fondation pour la recherche médicale, “Tout savoir sur les troubles du rythme cardiaque”, consulté le 2 avril 2021
[3] Bailly Vétérinaires, L’électrocardiogramme chez le cheval, consulté le 02 avril 2021
[4] M. de Lagarde, Prévalence des arythmies cardiaques liées à l’effort chez le trotteur, Thèse Vétérinaire, Ecole nationale vétérinaire d’Alfort, 2007